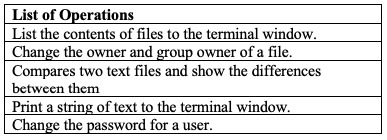
CS604 Quiz#2 Solution and discussion
-
The integer value of _________ semaphores can not be greater than 1.
►Counting
►Binary (Page 117)
►Mutex
►Bounded buffer -
The integer value of ________semaphores can range over an unrestricted integer domain.
►Counting (Page 117)
►Binary
►Mutex
►Bounded buffer -
The main memory is usually divided into partitions, one for __________ and other for __________.
- Operating System, User processes
- Operating system, CPU
- Processes, Virtual Memory
- Base Register, Limit Register
-
Using hardware solution to synchronization for complex problems, introduce a new synchronization tool know as _______________.
- TestAndSet
- Semaphore (Page 111)
- Swap
- Trap
-
We can use semaphores to deal with the number of __________process critical section problem.
►n-process critical section problem
-
Software solution to critical section problem can run only in environment ______________.
Multiprocessor
Multithreading
Uniprocessor
Separate address spacingThe software-based solution is 2 processes also they are not guaranteed to work on modern computers architecture. The critical section problem could be solved simply in a uniprocessor environment if we prevent interrupts from occurring from uniprocessor environment.
-
While executing the statement c++/c-- in Producer-Consumer problem, at back end certain number of
instructions are executed, if interleaving of statements happen, it create race condition. Tell number of
instructions that require “no interleaving” while executing c++/c–?3
1
2
0 -
A program can not execute unless whole or necessary part of it resides in the main memory. CS604
TRUE (Page 12)

@zaasmi said in CS604 Quiz#2 Solution and discussion:
A program can not execute unless whole or necessary part of it resides in the main memory.
Explanation:
The statement describes a fundamental concept in computing related to how programs are executed in a computer system. Specifically, it highlights that:
“A program cannot execute unless the whole or necessary part of it resides in the main memory.”
Explanation:
-
Main Memory (RAM) Requirements:
- For a program to run, it must be loaded into the computer’s main memory (RAM). The CPU (Central Processing Unit) can only directly access data and instructions stored in RAM. If a program or a part of it is not in RAM, the CPU cannot execute it.
-
Execution Process:
- When a program is executed, the operating system loads the necessary portions of the program from secondary storage (like a hard drive or SSD) into RAM. This loading process includes the program’s executable code, data, and other required resources.
-
Partial Loading:
- In some systems, especially with virtual memory and paging, only parts of a program may be loaded into RAM initially. The rest of the program can be loaded on-demand as needed. However, at any given time, the parts of the program currently being executed must be present in RAM.
-
Swapping and Paging:
- Operating systems use techniques like swapping (moving entire processes between RAM and disk) and paging (dividing memory into pages and swapping pages in and out of RAM) to manage memory efficiently. Despite these techniques, the CPU requires the relevant pages or parts of the program to be in RAM to execute instructions.
In summary, for a program to execute, it must be fully or partially loaded into the main memory (RAM) because the CPU requires direct access to memory to perform computations and process instructions.
-